SINGLE SITE CONVENTIONAL
This city hotel must offer excellent customer service if it is to succeed. Guests need to feel safe, secure and well cared-for. The hotel has installed a MOTOTRBO repeater on the premises, giving excellent coverage all the way from the basement to the penthouse suite. Now, with their Work Order Ticket Management system and MOTOTRBO SL4000e radios, the staff have the tools they need to deliver a top-class guest experience. A repeater brings many benefits to your workplace communications. With high transmitter power and a sensitive receiver, your coverage area is significantly boosted. The digital error correction capability within the unit also improves voice quality. And with the MOTOTRBO repeater IP interface, you can more efficiently implement operations-critical applications such as Work Order Ticketing, GPS Dispatch Consoles and Telephone Interconnect. MOTOTRBO repeaters use both TDMA timeslots of a DMR standard radio channel. Depending on user activity, this can support up to 200 radio users.

The development of modern conventional radio stations and communications controllers has made it possible to bring the service capabilities of the usual equipment to the trunking capabilities closer, allowing the creation of small systems with enhanced capabilities. Thus, in spite of the rapid development of trunking systems around the world, conventional communication remains a fiscal decision and continues to evolve.
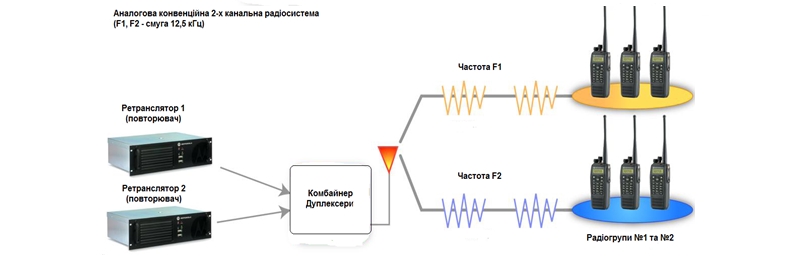
In fact, any conventional radio system is based on the use of repeaters (repeaters). This requires the presence of two frequencies (duplex pair), which are received in the UDCP SE in accordance with the current legislation. The first reason for using a repeater is the ability to significantly increase the range of radio communication. Linking two radio stations without a repeater is at best possible at a distance of only a few kilometers, while the repeater allows you to increase the range to tens of kilometers. When using the MotoTRBO equipment, there is always the possibility of flexible scaling and increase of the capacity of the existing radio communication system.
Main benefits of MotoTRBO equipment DMR standard:
1. Increased efficiency of frequency resource use
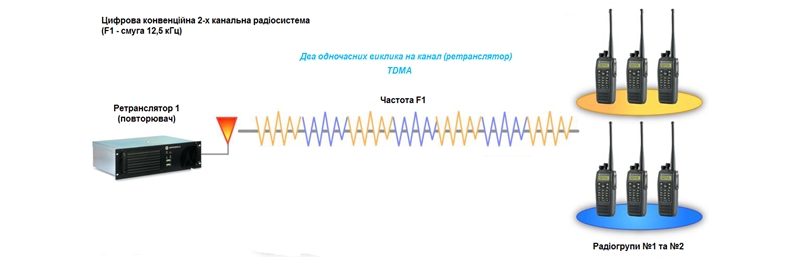
For many users of two-way radio systems, the greatest advantage of digital standards is that they allow more efficient use of the resource of existing licensed channels. Ether is becoming more and more loaded, and former licensed channel structures, originally designed to service a small number of users, are no longer able to cope with increasing traffic. To increase the efficiency of frequency resource use, the DMR protocol (ETSI) uses the method of dividing a channel in the width of 12.5 kHz into two timelosses using TDMA technology. This allows you to save the operating characteristics of the bandwidth of 12.5 kHz and at the same time makes it possible, in a universal way, depending on the current needs, to connect a significantly larger number of subscribers with existing licensed channels in the organization. For example, two intervals in one channel can be used to transfer two separate calls. You can also select one of the call intervals, and in the second one, you can transfer data or priority traffic simultaneously.
2. Longer battery life
One of the main characteristics of mobile terminals has always been the battery life between charging. Previously, there were only two ways to increase the device's operating time on a single battery charge. The first is to increase the capacity of the battery. Manufacturers of batteries have already done a lot to increase the capacity of their products, but further improvement of the characteristics at this time is possible only by increasing the size, and hence at the expense of portability. Another way is to reduce the power of the transmitter, part of the portable terminal, with the highest power consumption. However, this will result in a narrowing of its zone of operation and the potential for interference from other devices, which is an unacceptable compromise for the professional system.
The DMR ETSI standard offers another, rather effective option. Since one call only takes one of the two TDMA timeslots, it only needs half the power of the transmitter. Half of the time in the unused TDMA time slot is in the standby mode. With typical workload "5% reception, 5% transfer, 90% wait" 80% of battery charge is spent during transmission. The two-month TDMA protocol reduces the real time of the transmitter by half, thereby saving up to 40% battery charge, which helps to increase battery life in talk mode. As a result, the overall battery consumption during calls is greatly reduced, which allows for longer use of the terminal from one charge. In addition, the ETSI DMR provides power management and standby power management technologies that further enhance battery life.
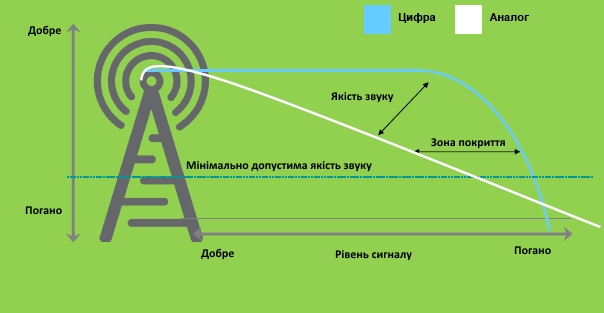
3. Improved speech quality, extended area of operation
Conventional system MotoTRBO allows you to implement the following functions in digital mode:
- General call (connection to all subscribers within the same repeater)
- Group call
- Individual challenge
- Text messages
- Emergency call (possibility to engage in any logical communication channel for the purpose of urgent notification of the subscriber or group)
- Radio kill (the ability to kill a radio station, that is, to shut it off remotely from a communications system, which is convenient, for example, in the case of its theft or interception by attackers)
- Radio check (possibility to remotely check the presence of a radio station in the system)
- AVL (Automatic Vehicle Location - GPS position monitoring station)
- Telemetry (remote measurement and data collection for operator or user)
- Encoding voice and data on basic (16 bit) or upgraded levels (40 bit)
DIMENSIONS
• 1 Site
• 1 Repeater
• Up to 200 Radios (recommended 100 Radios )

19 March 2019